Once we’ve confirmed that Gulp is installed in our project:
we are ready to start using Gulp to see what it can do.
Step 1: Create a gulpfile.js file
In the root directory of our project, we need to create a file called “gulpfile.js”. This file will contain all of our Gulp task definitions. Add this line to the top of the file, which essentially “imports” the gulp package:
var gulp = require('gulp');
Then type this command in the bash window:
gulp
Notice that gulp is looking for a ‘default’ task.
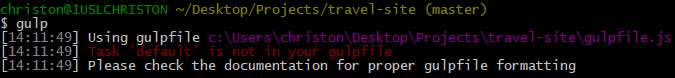
Step 2: Create a default task
Now add this code to the gulpfile.js:
gulp.task('default', function() {
console.log("Hooray- you created a Gulp task.")
});
Then run the gulp command again:
gulp
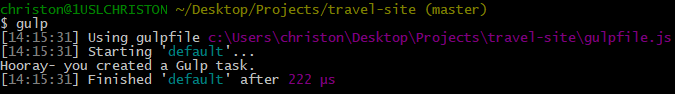
Notice that since this is the default gulp task, I didn’t need to specify the task in the command window. Just ‘gulp’ is all it took to execute this task.
Step 3: Create a named task
Add this code to the gulpfile.js:
gulp.task('html', function() {
console.log("Imagine something useful being done to your HTML here.")
});
Then run this gulp command. Notice that I used the name of the task in the command this time:
gulp html
Which yields:
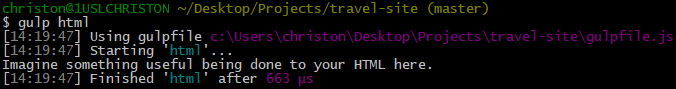
For more information about using Gulp, see:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/gulp/index.htm